Textile Sample
1937 (made)
| Artist/Maker | |
| Place of origin |
Ankara is a printed cotton cloth, produced in a variety of patterns formed by the layering of polychromatic dyes. Fashionable in West and East Africa since the late 19th century, ankara is variously known as 'African wax' or 'Dutch wax' print – despite wax rarely being used in its manufacture. Embodying the overlapping colonial interests that prevailed in the region and beyond, the cloth has a complex history – rooted in trade monopolisation and cultural appropriation, yet acting as a conduit for African agency and resistance.
Originally produced in the Netherlands, ankara emerged from experiments to mechanically replicate batik, an Indonesian wax-print cloth traditionally developed by hand. Early Dutch attempts roller-printed a resin-resist onto both sides of the cloth before dyeing; the resist was then washed out, with additional layers of colour added by repeating this process, hand-blocking and/or roller-printing. The intended export market of Indonesia did not respond well to this imitation batik, as the resin was prone to cracking and bubbling, producing defects in the print. A keen market for the cloth did, however, emerge across West Africa in the 1890s, such that several factories – chiefly in Britain and the Netherlands – began producing ankara with this new customer in mind. Responding to market feedback on popular colours and patterns, European producers adapted ankara designs to suit the tastes of their discerning West African customers. In a collaboration between the consumer, dealer and manufacturer, local sellers would inform European merchants which styles were in demand and suggest motifs that would likely sell well.
By the early 20th century, a cheaper and more refined method of ankara production had been developed. Sometimes called 'fancy prints', these ankara are roller-printed with a design on one side of the cloth only, eschewing the use of a resin-resist. Many examples of this later ankara purposefully include the imperfections that originally marred Dutch attempts to replicate batik – alluding to the more esteemed resin-resist technique. Decades after its arrival, independence from colonial rule saw the production of ankara relocate to the continent, when African competitors established their own rival businesses. Ankara designs during this time often featured political symbols and slogans, celebrating a new era of independence. For many, ankara remains a powerful signifier of West African identity, reinforcing personal style and national pride.
Originally produced in the Netherlands, ankara emerged from experiments to mechanically replicate batik, an Indonesian wax-print cloth traditionally developed by hand. Early Dutch attempts roller-printed a resin-resist onto both sides of the cloth before dyeing; the resist was then washed out, with additional layers of colour added by repeating this process, hand-blocking and/or roller-printing. The intended export market of Indonesia did not respond well to this imitation batik, as the resin was prone to cracking and bubbling, producing defects in the print. A keen market for the cloth did, however, emerge across West Africa in the 1890s, such that several factories – chiefly in Britain and the Netherlands – began producing ankara with this new customer in mind. Responding to market feedback on popular colours and patterns, European producers adapted ankara designs to suit the tastes of their discerning West African customers. In a collaboration between the consumer, dealer and manufacturer, local sellers would inform European merchants which styles were in demand and suggest motifs that would likely sell well.
By the early 20th century, a cheaper and more refined method of ankara production had been developed. Sometimes called 'fancy prints', these ankara are roller-printed with a design on one side of the cloth only, eschewing the use of a resin-resist. Many examples of this later ankara purposefully include the imperfections that originally marred Dutch attempts to replicate batik – alluding to the more esteemed resin-resist technique. Decades after its arrival, independence from colonial rule saw the production of ankara relocate to the continent, when African competitors established their own rival businesses. Ankara designs during this time often featured political symbols and slogans, celebrating a new era of independence. For many, ankara remains a powerful signifier of West African identity, reinforcing personal style and national pride.
Object details
| Categories | |
| Object type | |
| Materials and techniques | cotton, printing |
| Brief description | Textile sample, printed cotton fabric, manufactured by Logan, Muckelt & Co., Manchester, England, 1937 |
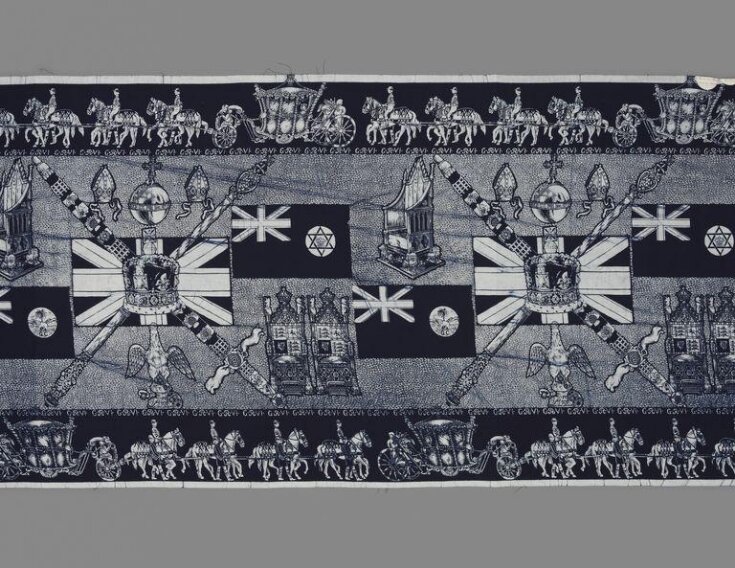
| Physical description | Textile sample of printed cotton in blue and white, featuring colonial imagery and motifs such as the Union Jack flag, coronation throne, mitre, crown, orb, spectre, sword, and a coronation procession including horses and royal carriage. Made to commemorate the Coronation of King George VI in 1937. |
| Dimensions |
|
| Credit line | Given by the Manchester Design Registry |
| Object history | Registered number 370(23). |
| Production | Logan, Muckelt and Co. is one of several companies - principally British or Dutch - who in the early 20th century designed, printed, exported and/or distributed factory-printed cotton textiles for the West African market. Established in 1884 and based in Manchester, England, the company designed, printed and dyed pre-made cloth specifically for the African market. |
| Summary | Ankara is a printed cotton cloth, produced in a variety of patterns formed by the layering of polychromatic dyes. Fashionable in West and East Africa since the late 19th century, ankara is variously known as 'African wax' or 'Dutch wax' print – despite wax rarely being used in its manufacture. Embodying the overlapping colonial interests that prevailed in the region and beyond, the cloth has a complex history – rooted in trade monopolisation and cultural appropriation, yet acting as a conduit for African agency and resistance. Originally produced in the Netherlands, ankara emerged from experiments to mechanically replicate batik, an Indonesian wax-print cloth traditionally developed by hand. Early Dutch attempts roller-printed a resin-resist onto both sides of the cloth before dyeing; the resist was then washed out, with additional layers of colour added by repeating this process, hand-blocking and/or roller-printing. The intended export market of Indonesia did not respond well to this imitation batik, as the resin was prone to cracking and bubbling, producing defects in the print. A keen market for the cloth did, however, emerge across West Africa in the 1890s, such that several factories – chiefly in Britain and the Netherlands – began producing ankara with this new customer in mind. Responding to market feedback on popular colours and patterns, European producers adapted ankara designs to suit the tastes of their discerning West African customers. In a collaboration between the consumer, dealer and manufacturer, local sellers would inform European merchants which styles were in demand and suggest motifs that would likely sell well. By the early 20th century, a cheaper and more refined method of ankara production had been developed. Sometimes called 'fancy prints', these ankara are roller-printed with a design on one side of the cloth only, eschewing the use of a resin-resist. Many examples of this later ankara purposefully include the imperfections that originally marred Dutch attempts to replicate batik – alluding to the more esteemed resin-resist technique. Decades after its arrival, independence from colonial rule saw the production of ankara relocate to the continent, when African competitors established their own rival businesses. Ankara designs during this time often featured political symbols and slogans, celebrating a new era of independence. For many, ankara remains a powerful signifier of West African identity, reinforcing personal style and national pride. |
| Collection | |
| Accession number | CIRC.372-1966 |
About this object record
Explore the Collections contains over a million catalogue records, and over half a million images. It is a working database that includes information compiled over the life of the museum. Some of our records may contain offensive and discriminatory language, or reflect outdated ideas, practice and analysis. We are committed to addressing these issues, and to review and update our records accordingly.
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
| Record created | June 24, 2009 |
| Record URL |
Download as: JSON