Architectural Drawing
Ca.1990
| Artist/Maker | |
| Place of origin |
Located in a residential area of Harringay, North London, St Paul’s was designed by Peter Jenkins between 1988 and 1993 to replace a Victorian Gothic Revival church (built 1890-1) which was destroyed by fire on Ash Wednesday 1984.
Jenkins’ church combines traditional liturgical forms with contemporary design. The plan of the church is traditional, being narrow and rectangular with the entrance at the west end and the altar at the east. This was in part dictated by the confines of the site, but also by the church’s Anglo-Catholic liturgical tradition which preferred an axial, processional plan. This traditional plan is in contrast to the majority of contemporary churches, which locate congregations around a central altar in order to emphasise the participatory aspect of the Communion.
In scale, Jenkins’ design echoes that of its Victorian predecessor, which was built to a vast scale, able to seat 900, and visually dominated the area’s skyline. Despite being a much smaller church in capacity, seating just 140, Jenkins has maintained the church’s visual dominance, making it an architectural and spiritual focal point in the surrounding area. This aspect of the design generated serious opposition from the local council, which argued – unsuccessfully – that the new church should blend in with the surrounding architecture.
Jenkins’ church combines traditional liturgical forms with contemporary design. The plan of the church is traditional, being narrow and rectangular with the entrance at the west end and the altar at the east. This was in part dictated by the confines of the site, but also by the church’s Anglo-Catholic liturgical tradition which preferred an axial, processional plan. This traditional plan is in contrast to the majority of contemporary churches, which locate congregations around a central altar in order to emphasise the participatory aspect of the Communion.
In scale, Jenkins’ design echoes that of its Victorian predecessor, which was built to a vast scale, able to seat 900, and visually dominated the area’s skyline. Despite being a much smaller church in capacity, seating just 140, Jenkins has maintained the church’s visual dominance, making it an architectural and spiritual focal point in the surrounding area. This aspect of the design generated serious opposition from the local council, which argued – unsuccessfully – that the new church should blend in with the surrounding architecture.
Object details
| Categories | |
| Object type | |
| Materials and techniques | Pencil on tracing paper. |
| Brief description | Preliminary sketches for St. Paul's Church, Harringay with annotations, pencil on tracing paper, by Peter Jenkins, ca.1990. |
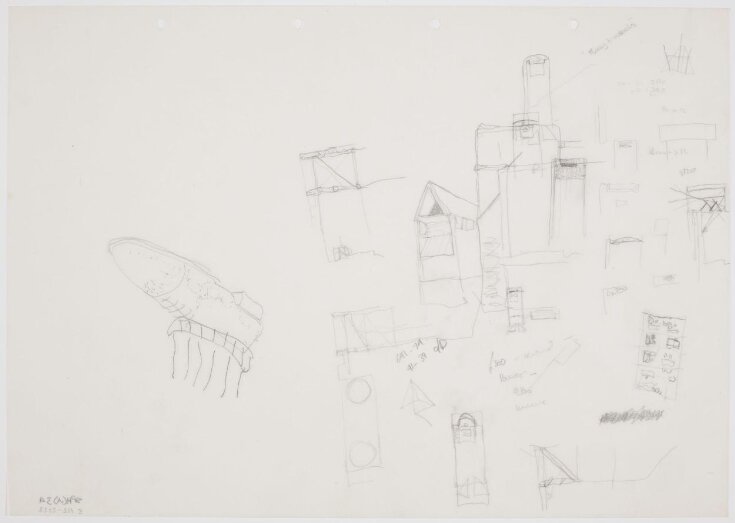
| Physical description | Preliminary sketches shown alongside a drawing of a shoe. |
| Dimensions |
|
| Credit line | Given by Peter Jenkins |
| Place depicted | |
| Summary | Located in a residential area of Harringay, North London, St Paul’s was designed by Peter Jenkins between 1988 and 1993 to replace a Victorian Gothic Revival church (built 1890-1) which was destroyed by fire on Ash Wednesday 1984. Jenkins’ church combines traditional liturgical forms with contemporary design. The plan of the church is traditional, being narrow and rectangular with the entrance at the west end and the altar at the east. This was in part dictated by the confines of the site, but also by the church’s Anglo-Catholic liturgical tradition which preferred an axial, processional plan. This traditional plan is in contrast to the majority of contemporary churches, which locate congregations around a central altar in order to emphasise the participatory aspect of the Communion. In scale, Jenkins’ design echoes that of its Victorian predecessor, which was built to a vast scale, able to seat 900, and visually dominated the area’s skyline. Despite being a much smaller church in capacity, seating just 140, Jenkins has maintained the church’s visual dominance, making it an architectural and spiritual focal point in the surrounding area. This aspect of the design generated serious opposition from the local council, which argued – unsuccessfully – that the new church should blend in with the surrounding architecture. |
| Bibliographic reference | Taken from notes by Peter Jenkins (Clare Lodge, Practice Archivist, 25/02/2026)
Studies of the triangular wind girder roof on A3 tracing paper concentrating on the east end and sanctuary with the apsidal form, not yet rejected (lower right centre) but the plan shows the emergence of the triangular towers at the west end. Light reflector studies explore transverse angled reflectors (mid right) and a dropped nave-wide lay light at a level below the roof girder over the altar and top lighting a single transverse stairway down to the sacristy beyond the reredos wall of the sanctuary (mid upper section and perspective view from the northeast). Note the emergence in the left hand sections of the steel wind girder roof framing being developed with the structural engineer, the late Michael Courtney of Ove Arup. (The inverted drawing of a shoe and foot on the left was made to show a young assistant and completely irrelevant to the project, ‘co-respondent shoes’.) |
| Other number | SPH(A)34 - Previous number |
| Collection | |
| Accession number | E.122-2022 |
About this object record
Explore the Collections contains over a million catalogue records, and over half a million images. It is a working database that includes information compiled over the life of the museum. Some of our records may contain offensive and discriminatory language, or reflect outdated ideas, practice and analysis. We are committed to addressing these issues, and to review and update our records accordingly.
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
| Record created | June 10, 2019 |
| Record URL |
Download as: JSONIIIF Manifest