Boric Acid
Design
1951 (made)
1951 (made)
| Artist/Maker | |
| Place of origin |
Sir William Henry Bragg and his son William were awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1915 for the invention of X-ray crystallography. This new science enabled the first drawings of the arrangement of atoms within molecules. It was particularly developed as one of the most significant and exciting branches of science during the late 1940s and put Britain at the cutting edge of international research. In 1946 Dr Helen Megaw, a Crystallographer (Crystallography - a study of the structure of matter) suggested that the patterns made by X-ray crystallography could be used as a fresh source of inspiration for wallpaper and fabric designers. The patterns were considered particularly appropriate for use in textile design because of their repetitive symmetry and natural beauty.
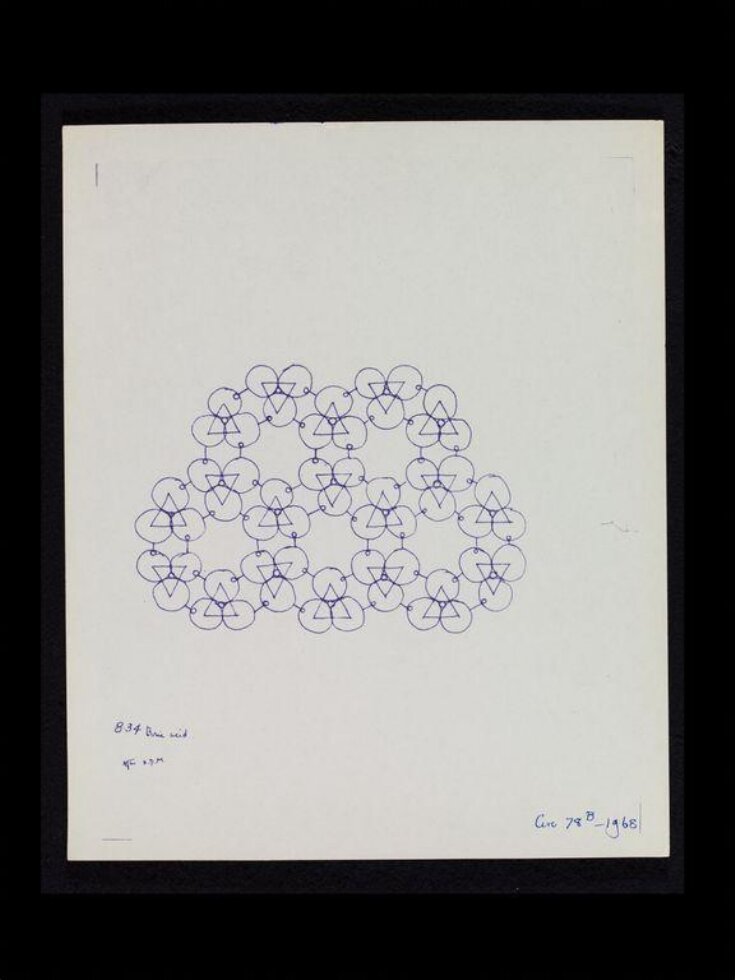
The Festival of Britain held in 1951 provided new opportunities for textile design and manufacture. This diagram of Boric acid, a widely used antispetic and insecticide, is one of a group of crystal structure drawings that inspired textiles made by the Festival Pattern Group for the event. The idea of patterns inspired by science was perfect for the theme of the Festival which had been planned as a ‘combined exhibition of science, technology and industrial design’.
The Festival of Britain held in 1951 provided new opportunities for textile design and manufacture. This diagram of Boric acid, a widely used antispetic and insecticide, is one of a group of crystal structure drawings that inspired textiles made by the Festival Pattern Group for the event. The idea of patterns inspired by science was perfect for the theme of the Festival which had been planned as a ‘combined exhibition of science, technology and industrial design’.
Object details
| Categories | |
| Object type | |
| Title | Boric Acid (assigned by artist) |
| Materials and techniques | Ink on paper |
| Brief description | Design for the 1951 Crystal Design Project for the Festival of Britain |
| Physical description | Design in dye-line print on paper of a pattern based upon a cell structure diagram |
| Dimensions |
|
| Production type | Design |
| Marks and inscriptions | 8.34 BORIC ACID after N.D.M |
| Credit line | Given by the Council of Industrial Design |
| Object history | Boric acid, also called boracic acid or orthoboric acid or Acidum Boricum, is a mild acid often used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, in nuclear power plants to control the fission rate of uranium, and as a precursor of other chemical compounds. It exists in the form of colorless crystals or a white powder and dissolves in water. It has the chemical formula H3BO3, sometimes written B(OH)3. When occurring as a mineral, it is called sassolite. X-ray crystallography involved projecting a narrow beam of X-rays on to crystalline material. Photographs were then taken of the diffracted X-rays, and the resulting lines or spots were used to plot ‘maps’ indicating the relationships between atoms. For the first time ever it enabled scientist to work out the structure of atoms within molecules. Britain was a world leader in the field of crystallography and during the post war period this was one of the most significant and stimulating branches of science. |
| Association | |
| Summary | Sir William Henry Bragg and his son William were awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1915 for the invention of X-ray crystallography. This new science enabled the first drawings of the arrangement of atoms within molecules. It was particularly developed as one of the most significant and exciting branches of science during the late 1940s and put Britain at the cutting edge of international research. In 1946 Dr Helen Megaw, a Crystallographer (Crystallography - a study of the structure of matter) suggested that the patterns made by X-ray crystallography could be used as a fresh source of inspiration for wallpaper and fabric designers. The patterns were considered particularly appropriate for use in textile design because of their repetitive symmetry and natural beauty. The Festival of Britain held in 1951 provided new opportunities for textile design and manufacture. This diagram of Boric acid, a widely used antispetic and insecticide, is one of a group of crystal structure drawings that inspired textiles made by the Festival Pattern Group for the event. The idea of patterns inspired by science was perfect for the theme of the Festival which had been planned as a ‘combined exhibition of science, technology and industrial design’. |
| Bibliographic reference | Taken from Departmental Circulation Register 1968 |
| Collection | |
| Accession number | CIRC.78B-1968 |
About this object record
Explore the Collections contains over a million catalogue records, and over half a million images. It is a working database that includes information compiled over the life of the museum. Some of our records may contain offensive and discriminatory language, or reflect outdated ideas, practice and analysis. We are committed to addressing these issues, and to review and update our records accordingly.
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
| Record created | November 21, 2007 |
| Record URL |
Download as: JSON