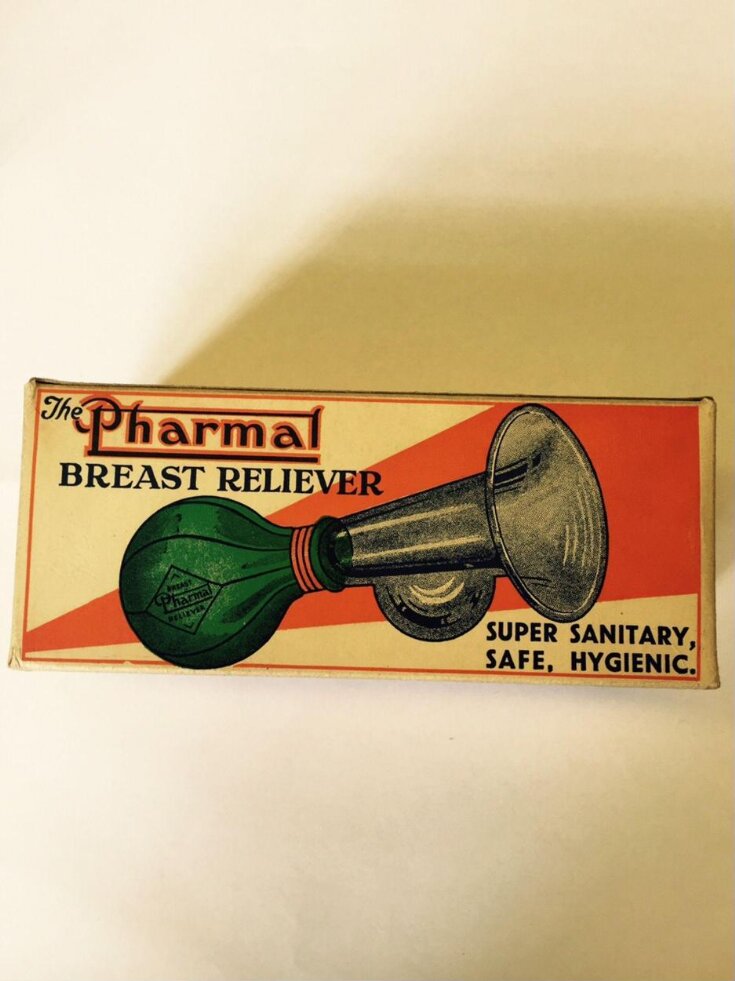
The Pharmal Breast Reliever
Breast Pump
1960-1969 (Manufactured)
1960-1969 (Manufactured)
| Artist/Maker | |
| Place of origin |
There has been a long history of artificially feeding babies. This has been for a number of reasons such as, the mothers’ choice, problems with breast feeding; mother’s dying in childbirth or a sickly child to weak to suckle, ways around tradition feeding have included wet nursing, bottle/vessel feeding and the use of animal’s milk or formula. Wet nursing was one of the most common methods of feeding infants, it was seen as a profession and the wet nurses would have had contracts with the families they worked for. It was popular from 2000bc to the nineteenth century, it was mainly used by higher ranking women in society, but when attitudes changed towards the use of wet nurses vessel feeding took over.
Feeding vessels have been found dating as far back as 2000 BC, these early vessels would have been used to fed babies animal’s milk. The pap boat was introduced in the sixteenth century, used to feed infants a mixture of bread and milk or water known as pap. These like other feeding vessels were difficult to clean and the poor hygiene of these led to the deaths of many artificially fed babies.
It was not until the nineteenth century that there was a great advance in the development of feeding bottles. These were generally made of glass and used teats, rubber teats were introduced in 1845. The boat shaped (banana) bottle was developed in England in 1896, these were open ended that allowed airflow and a teat at one end.
Animal milk was most commonly used for artificial feeding until the nineteenth century. The first chemical analysis of human milk was in 1760 by Jean Charles Des-Essartz, he published the results in his Treaties of physical upbringing of Children, which declared mother’s milk was best. The first formula was patented in 1865 by the chemist Justus Von Liebig, he produced it first in a liquid then later a powder. Another development that had been patented earlier was evaporated milk, which was a popular choice for feeding to babies in bottles; it was particularly popular and came highly recommended by doctors in the 1930s and 1940s.
By the end of the nineteenth century there were 27 brands of formula available. The public were also well aware of the germ theory and accepted the need for cleanliness. This led to the improved safety of using artificial feeding and for a time it was seen as better choice for the child than breastfeeding, which saw a decline until the 1970s.
Feeding vessels have been found dating as far back as 2000 BC, these early vessels would have been used to fed babies animal’s milk. The pap boat was introduced in the sixteenth century, used to feed infants a mixture of bread and milk or water known as pap. These like other feeding vessels were difficult to clean and the poor hygiene of these led to the deaths of many artificially fed babies.
It was not until the nineteenth century that there was a great advance in the development of feeding bottles. These were generally made of glass and used teats, rubber teats were introduced in 1845. The boat shaped (banana) bottle was developed in England in 1896, these were open ended that allowed airflow and a teat at one end.
Animal milk was most commonly used for artificial feeding until the nineteenth century. The first chemical analysis of human milk was in 1760 by Jean Charles Des-Essartz, he published the results in his Treaties of physical upbringing of Children, which declared mother’s milk was best. The first formula was patented in 1865 by the chemist Justus Von Liebig, he produced it first in a liquid then later a powder. Another development that had been patented earlier was evaporated milk, which was a popular choice for feeding to babies in bottles; it was particularly popular and came highly recommended by doctors in the 1930s and 1940s.
By the end of the nineteenth century there were 27 brands of formula available. The public were also well aware of the germ theory and accepted the need for cleanliness. This led to the improved safety of using artificial feeding and for a time it was seen as better choice for the child than breastfeeding, which saw a decline until the 1970s.
Object details
| Category | |
| Object type | |
| Parts | This object consists of 2 parts.
|
| Title | The Pharmal Breast Reliever (manufacturer's title) |
| Materials and techniques | glass, rubber and card |
| Brief description | The Pharmal Breast Reliver, boxed breast pump made of glass and rubber ca 1960 |
| Physical description | A box breast reliever. A clear glass vile with a bulbous shape in the middle and a red rubber pump attached to the end. There is a gold coloured trim where the rubber meets the glass. The rubber pump is also stamped with the words Breast Pharmal Reliever inside a diamond shape. The box is printed on all sides mainly in reds and greens. The front of the box has a picture of the breast reliever on it with the title above and the words Super, Sanitary, Safe, Hygienic underneath. |
| Dimensions |
|
| Production type | Mass produced |
| Marks and inscriptions | The Pharmal Breast Reliever
Super, Sanitary, Safe, Hygienic
The receiver on the new "Pharmal" Breast Reliever is one of the latest pattern. Specially manufactured to facilitate cleaning.
It is sanitary, safe and hygienic. All the difficulty met with in cleaning out the ordinary bulb shape receiver is entirely obviated. |
| Credit line | Given by Susan McKean |
| Summary | There has been a long history of artificially feeding babies. This has been for a number of reasons such as, the mothers’ choice, problems with breast feeding; mother’s dying in childbirth or a sickly child to weak to suckle, ways around tradition feeding have included wet nursing, bottle/vessel feeding and the use of animal’s milk or formula. Wet nursing was one of the most common methods of feeding infants, it was seen as a profession and the wet nurses would have had contracts with the families they worked for. It was popular from 2000bc to the nineteenth century, it was mainly used by higher ranking women in society, but when attitudes changed towards the use of wet nurses vessel feeding took over. Feeding vessels have been found dating as far back as 2000 BC, these early vessels would have been used to fed babies animal’s milk. The pap boat was introduced in the sixteenth century, used to feed infants a mixture of bread and milk or water known as pap. These like other feeding vessels were difficult to clean and the poor hygiene of these led to the deaths of many artificially fed babies. It was not until the nineteenth century that there was a great advance in the development of feeding bottles. These were generally made of glass and used teats, rubber teats were introduced in 1845. The boat shaped (banana) bottle was developed in England in 1896, these were open ended that allowed airflow and a teat at one end. Animal milk was most commonly used for artificial feeding until the nineteenth century. The first chemical analysis of human milk was in 1760 by Jean Charles Des-Essartz, he published the results in his Treaties of physical upbringing of Children, which declared mother’s milk was best. The first formula was patented in 1865 by the chemist Justus Von Liebig, he produced it first in a liquid then later a powder. Another development that had been patented earlier was evaporated milk, which was a popular choice for feeding to babies in bottles; it was particularly popular and came highly recommended by doctors in the 1930s and 1940s. By the end of the nineteenth century there were 27 brands of formula available. The public were also well aware of the germ theory and accepted the need for cleanliness. This led to the improved safety of using artificial feeding and for a time it was seen as better choice for the child than breastfeeding, which saw a decline until the 1970s. |
| Collection | |
| Accession number | B.113:1 & 2 -2014 |
About this object record
Explore the Collections contains over a million catalogue records, and over half a million images. It is a working database that includes information compiled over the life of the museum. Some of our records may contain offensive and discriminatory language, or reflect outdated ideas, practice and analysis. We are committed to addressing these issues, and to review and update our records accordingly.
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
| Record created | May 27, 2015 |
| Record URL |
Download as: JSONIIIF Manifest