Textile
ca. 1700 (made)
| Artist/Maker | |
| Place of origin |
Object Type
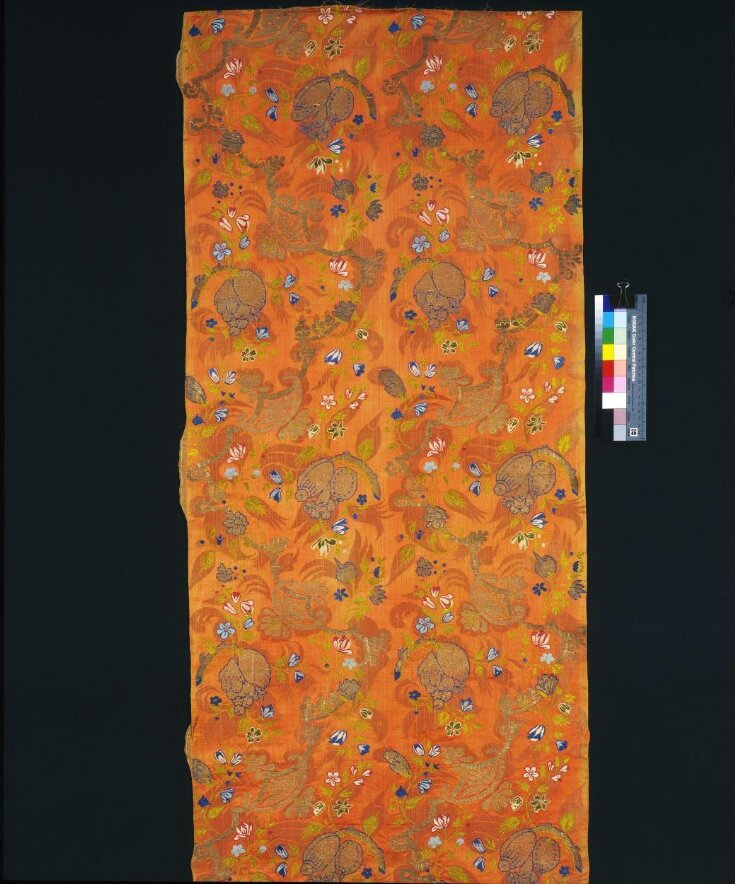
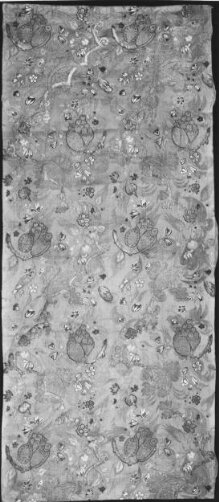
This length of woven silk was intended for clothing. It might have been chosen for a woman's gown or a man's waistcoat or nightgown, worn informally at home. The complexity of its woven structure would have made it expensive. Its bold pattern and distinctive colouring date it to a fairly brief period around 1700 when such a combination was highly fashionable.
Places
Dress silks from France began to dominate fashionable taste across Europe from the 1660s. The Minister of Finance, Jean-Baptiste Colbert (1619-1683), regulated the French textile industry to reduce the variety and improve the quality in each regional weaving centre. This was intended to help the centres compete against foreign imports, and to prevent their competing against each other. Lyon was the centre for the most complex and luxurious of the patterned silks. This example was probably woven there.
Design & Designing
In the late 17th and early 18th centuries the increasing import trade and other contacts between Asia and Europe greatly influenced the design of fashionable silks such as this. As well as the textiles themselves in clear, bright colours, other goods such as porcelain and lacquer lent shapes and motifs to the silk designers' repertoire. Books on natural history were a source for illustrations of unfamiliar flowers and fruit, fish, birds and other creatures.
This length of woven silk was intended for clothing. It might have been chosen for a woman's gown or a man's waistcoat or nightgown, worn informally at home. The complexity of its woven structure would have made it expensive. Its bold pattern and distinctive colouring date it to a fairly brief period around 1700 when such a combination was highly fashionable.
Places
Dress silks from France began to dominate fashionable taste across Europe from the 1660s. The Minister of Finance, Jean-Baptiste Colbert (1619-1683), regulated the French textile industry to reduce the variety and improve the quality in each regional weaving centre. This was intended to help the centres compete against foreign imports, and to prevent their competing against each other. Lyon was the centre for the most complex and luxurious of the patterned silks. This example was probably woven there.
Design & Designing
In the late 17th and early 18th centuries the increasing import trade and other contacts between Asia and Europe greatly influenced the design of fashionable silks such as this. As well as the textiles themselves in clear, bright colours, other goods such as porcelain and lacquer lent shapes and motifs to the silk designers' repertoire. Books on natural history were a source for illustrations of unfamiliar flowers and fruit, fish, birds and other creatures.
Object details
| Category | |
| Object type | |
| Materials and techniques | Silk damask, brocaded in silks and silver-gilt thread |
| Brief description | silk, 1705-20, probably French |
| Physical description | Dress silk; silk damask brocaded in silks & silver gilt thread with a pattern of scrolls, flowers and fruit in colours and gold on a figured apricot-coloured ground. |
| Dimensions |
|
| Gallery label |
|
| Credit line | Given by J. B. Clarke-Thornhill |
| Object history | Probably woven in France |
| Summary | Object Type This length of woven silk was intended for clothing. It might have been chosen for a woman's gown or a man's waistcoat or nightgown, worn informally at home. The complexity of its woven structure would have made it expensive. Its bold pattern and distinctive colouring date it to a fairly brief period around 1700 when such a combination was highly fashionable. Places Dress silks from France began to dominate fashionable taste across Europe from the 1660s. The Minister of Finance, Jean-Baptiste Colbert (1619-1683), regulated the French textile industry to reduce the variety and improve the quality in each regional weaving centre. This was intended to help the centres compete against foreign imports, and to prevent their competing against each other. Lyon was the centre for the most complex and luxurious of the patterned silks. This example was probably woven there. Design & Designing In the late 17th and early 18th centuries the increasing import trade and other contacts between Asia and Europe greatly influenced the design of fashionable silks such as this. As well as the textiles themselves in clear, bright colours, other goods such as porcelain and lacquer lent shapes and motifs to the silk designers' repertoire. Books on natural history were a source for illustrations of unfamiliar flowers and fruit, fish, birds and other creatures. |
| Collection | |
| Accession number | T.166-1927 |
About this object record
Explore the Collections contains over a million catalogue records, and over half a million images. It is a working database that includes information compiled over the life of the museum. Some of our records may contain offensive and discriminatory language, or reflect outdated ideas, practice and analysis. We are committed to addressing these issues, and to review and update our records accordingly.
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
| Record created | March 27, 2003 |
| Record URL |
Download as: JSONIIIF Manifest