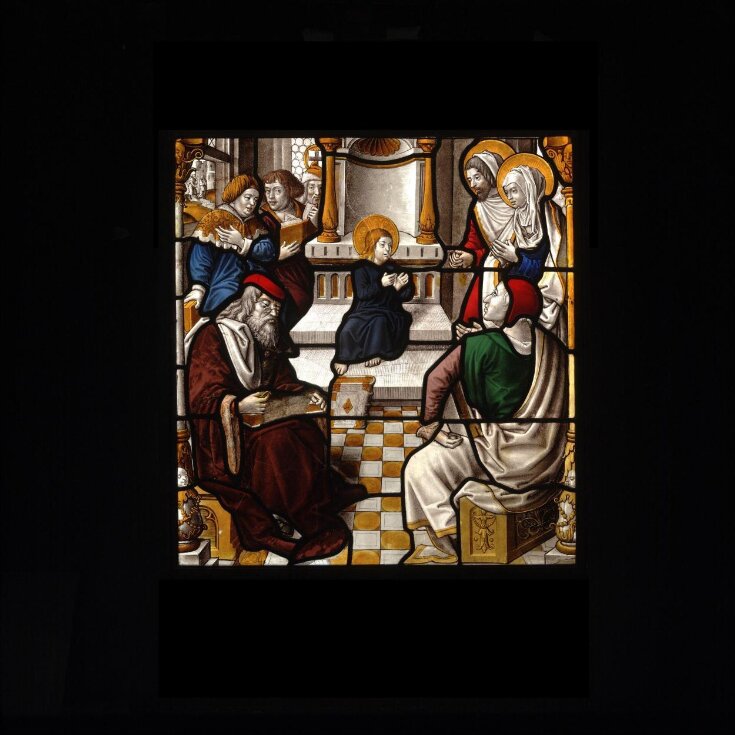
Christ amongst the Doctors
Panel
ca. 1522 to 1526 (made)
ca. 1522 to 1526 (made)
| Artist/Maker | |
| Place of origin |
This panel is one of many in the V&A that comes from the cloisters at Mariawald. These panels come from ten windows on the west and north sides of the cloister, plus one from the north end of the eastern part. The glazing of these cloisters began about 1510 and seem to have been completed in the 1530s.
Mariawald was a Cistercian abbey founded in 1480. The Cistercians were a monastic order established in 1098 in Burgundy at Citeaux. The founder of the Cistercians had broken away from the Benedictines which had been the first monastic order to be established in Europe, in the 6th century.
During the Revolutionary struggles in France and the subsequent religious upheavals under Napoleon, many monastic institutions on the continent were 'secularised' and their buildings destroyed. The abbey of Mariawald was closed down in 1802 but fortunately its buildings, including the cloisters, remain largely intact. However, the stained glass windows had been removed and it is believed that they were purchased by John Christopher Hampp of Norwich. Hampp sold the Mariawald panels to various churches and to private collectors. Many of these were purchased by the collector, Lord Brownlow who had them installed in his new chapel at Ashridge Park in Hertfordshire between 1811 and 1831.
In 1928 the contents of Ashridge Park were sold at auction and a private collector purchased the stained glass and gave it to the Victoria & Albert Museum.
W are able to reconstruct how the panels were placed in the cloister windows. Each window was composed of two openings ('lights'). Each light was composed of three large panels, plus one small tracery panel. So there would have been eight panels to each window.
From the surviving stained glass panels we can determine the theme of the cloister glazing. Each window had two panels depicting scenes from the Old Testament and two panels with scenes from the New Testament. Above the biblical story panels, were two smaller prophet (or 'messenger') panels. These contained half-images of Old Testament prophets holding scrolls with text relating to biblical passages connected with the scenes below. At the base of each window were donor and patron saint panels. These donors were the ones who contributed to the financing of the cloister glazing.
This type of narrative arrangement is known as 'typological'. Each Old Testament story was a 'type' or a prefigurement of a New Testament story ('antitype'). The prophets on each window would hold text from the Bible relating to the Old and New Testament stories. For example, this panel shows the New Testament story of 'Christ amongst the Doctors'. It was placed in the window just below that of the Old Testament scene of 'Joseph before Pharoah' (Museum No.C.119-1945). Just as Pharoah was impressed by the wisdom of Joseph, the young Christ overwhelmed the learned men of the Temple with his knowledge of the scriptures.
The typological arrangement was popular in the Middle Ages. The stories were reproduced in manuscripts and in engravings from woodcuts and collectively became known as 'Biblia Pauperum' ('Bibles of the Poor'). At the end of the 15th century the Biblia Pauperum were printed in book form and sold in their thousands. These books were used as design sources for artworks including stained glass panels.
Mariawald was a Cistercian abbey founded in 1480. The Cistercians were a monastic order established in 1098 in Burgundy at Citeaux. The founder of the Cistercians had broken away from the Benedictines which had been the first monastic order to be established in Europe, in the 6th century.
During the Revolutionary struggles in France and the subsequent religious upheavals under Napoleon, many monastic institutions on the continent were 'secularised' and their buildings destroyed. The abbey of Mariawald was closed down in 1802 but fortunately its buildings, including the cloisters, remain largely intact. However, the stained glass windows had been removed and it is believed that they were purchased by John Christopher Hampp of Norwich. Hampp sold the Mariawald panels to various churches and to private collectors. Many of these were purchased by the collector, Lord Brownlow who had them installed in his new chapel at Ashridge Park in Hertfordshire between 1811 and 1831.
In 1928 the contents of Ashridge Park were sold at auction and a private collector purchased the stained glass and gave it to the Victoria & Albert Museum.
W are able to reconstruct how the panels were placed in the cloister windows. Each window was composed of two openings ('lights'). Each light was composed of three large panels, plus one small tracery panel. So there would have been eight panels to each window.
From the surviving stained glass panels we can determine the theme of the cloister glazing. Each window had two panels depicting scenes from the Old Testament and two panels with scenes from the New Testament. Above the biblical story panels, were two smaller prophet (or 'messenger') panels. These contained half-images of Old Testament prophets holding scrolls with text relating to biblical passages connected with the scenes below. At the base of each window were donor and patron saint panels. These donors were the ones who contributed to the financing of the cloister glazing.
This type of narrative arrangement is known as 'typological'. Each Old Testament story was a 'type' or a prefigurement of a New Testament story ('antitype'). The prophets on each window would hold text from the Bible relating to the Old and New Testament stories. For example, this panel shows the New Testament story of 'Christ amongst the Doctors'. It was placed in the window just below that of the Old Testament scene of 'Joseph before Pharoah' (Museum No.C.119-1945). Just as Pharoah was impressed by the wisdom of Joseph, the young Christ overwhelmed the learned men of the Temple with his knowledge of the scriptures.
The typological arrangement was popular in the Middle Ages. The stories were reproduced in manuscripts and in engravings from woodcuts and collectively became known as 'Biblia Pauperum' ('Bibles of the Poor'). At the end of the 15th century the Biblia Pauperum were printed in book form and sold in their thousands. These books were used as design sources for artworks including stained glass panels.
Object details
| Categories | |
| Object type | |
| Title | Christ amongst the Doctors (generic title) |
| Materials and techniques | Stained glass |
| Brief description | Clear and coloured glass with painted details and yellow (silver) stain. Depicting the New Testament story of Christ Amongst the Doctors. From the cloisters of the abbey of Mariawald. Made in the workshop of Everhard Rensig or Gerhard Remisch. German (Lower Rhine), c.1522 to 1526. |
| Physical description | Christ sits on a step in front of an architectural structure which resembles an altar. In the room are five doctors with whom he has been discussing theology. On the right, Joseph and Mary approach towards him. |
| Dimensions |
|
| Credit line | Given by E.E. Cook Esquire. |
| Object history | Believed to be from the fifth window in the cloisters at Mariawald. |
| Historical context | Luke 2: 41-52 For the story of Christ amongst the doctors Mariawald was a Cistercian abbey founded in 1480. The Cistercians were a monastic order established in 1098 in Burgundy at Citeaux. The founder of the Cistercians had broken away from the Benedictines which had been the first monastic order to be established in Europe, in the 6th century. During the Revolutionary struggles in France and the subsequent religious upheavals under Napoleon, many monastic institutions on the continent were 'secularised' and their buildings destroyed. The abbey of Mariawald was closed down in 1802 but fortunately its buildings, including the cloisters, remain largely intact. However, the stained glass windows had been removed and it is believed that they were purchased by John Christopher Hampp of Norwich. Hampp sold the Mariawald panels to various churches and to private collectors. Many of these were purchased by the collector, Lord Brownlow who had them installed in his new chapel at Ashridge Park in Hertfordshire between 1811 and 1831. In 1928 the contents of Ashridge Park were sold at auction and a private collector purchased the stained glass and gave it to the Victoria & Albert Museum. This panel is one of many in the V&A that comes from the cloisters at Mariawald. These panels come from ten windows on the west and north sides of the cloister, plus one from the north end of the eastern part. The glazing of these cloisters began about 1510 and seem to have been completed in the 1530s. As the cloisters were never dismantled we can reconstruct how the panels were placed in the architectural structure. The window openings in the cloisters were each composed of two openings ('lights'). Each light was composed of three large panels, plus one small tracery panel. So there would have been eight panels to each window. From the surviving stained glass panels we can determine the theme of the cloister glazing. Each window had two panels depicting scenes from the Old Testament and two panels with scenes from the New Testament. Above the biblical story panels, were two smaller prophet (or 'messenger') panels. These contained half-images of Old Testament prophets holding scrolls with text relating to biblical passages connected with the scenes below. At the base of each window were donor and patron saint panels. These donors were the ones who contributed to the financing of the cloister glazing. This type of narrative arrangement is known as 'typological'. Each Old Testament story was a 'type' or a prefigurement of a New Testament story ('antitype'). For example, the Old Testament story of Elisha greeted by the Sons of the Prophet was a prefigurement of the New Testament 'Entry of Christ into Jerusalem' which occurred on what we now call 'Palm Sunday'. The typological arrangement was popular in the Middle Ages. The stories were reproduced in manuscripts and in engravings from woodcuts and collectively became known as 'Biblia Pauperum' ('Bibles of the Poor'). At the end of the 15th century the Biblia Pauperum were printed in book form and sold in their thousands. These books were used as design sources for artworks including stained glass panels. |
| Subjects depicted | |
| Literary references |
|
| Summary | This panel is one of many in the V&A that comes from the cloisters at Mariawald. These panels come from ten windows on the west and north sides of the cloister, plus one from the north end of the eastern part. The glazing of these cloisters began about 1510 and seem to have been completed in the 1530s. Mariawald was a Cistercian abbey founded in 1480. The Cistercians were a monastic order established in 1098 in Burgundy at Citeaux. The founder of the Cistercians had broken away from the Benedictines which had been the first monastic order to be established in Europe, in the 6th century. During the Revolutionary struggles in France and the subsequent religious upheavals under Napoleon, many monastic institutions on the continent were 'secularised' and their buildings destroyed. The abbey of Mariawald was closed down in 1802 but fortunately its buildings, including the cloisters, remain largely intact. However, the stained glass windows had been removed and it is believed that they were purchased by John Christopher Hampp of Norwich. Hampp sold the Mariawald panels to various churches and to private collectors. Many of these were purchased by the collector, Lord Brownlow who had them installed in his new chapel at Ashridge Park in Hertfordshire between 1811 and 1831. In 1928 the contents of Ashridge Park were sold at auction and a private collector purchased the stained glass and gave it to the Victoria & Albert Museum. W are able to reconstruct how the panels were placed in the cloister windows. Each window was composed of two openings ('lights'). Each light was composed of three large panels, plus one small tracery panel. So there would have been eight panels to each window. From the surviving stained glass panels we can determine the theme of the cloister glazing. Each window had two panels depicting scenes from the Old Testament and two panels with scenes from the New Testament. Above the biblical story panels, were two smaller prophet (or 'messenger') panels. These contained half-images of Old Testament prophets holding scrolls with text relating to biblical passages connected with the scenes below. At the base of each window were donor and patron saint panels. These donors were the ones who contributed to the financing of the cloister glazing. This type of narrative arrangement is known as 'typological'. Each Old Testament story was a 'type' or a prefigurement of a New Testament story ('antitype'). The prophets on each window would hold text from the Bible relating to the Old and New Testament stories. For example, this panel shows the New Testament story of 'Christ amongst the Doctors'. It was placed in the window just below that of the Old Testament scene of 'Joseph before Pharoah' (Museum No.C.119-1945). Just as Pharoah was impressed by the wisdom of Joseph, the young Christ overwhelmed the learned men of the Temple with his knowledge of the scriptures. The typological arrangement was popular in the Middle Ages. The stories were reproduced in manuscripts and in engravings from woodcuts and collectively became known as 'Biblia Pauperum' ('Bibles of the Poor'). At the end of the 15th century the Biblia Pauperum were printed in book form and sold in their thousands. These books were used as design sources for artworks including stained glass panels. |
| Bibliographic references |
|
| Collection | |
| Accession number | C.295-1928 |
About this object record
Explore the Collections contains over a million catalogue records, and over half a million images. It is a working database that includes information compiled over the life of the museum. Some of our records may contain offensive and discriminatory language, or reflect outdated ideas, practice and analysis. We are committed to addressing these issues, and to review and update our records accordingly.
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
| Record created | May 8, 2002 |
| Record URL |
Download as: JSONIIIF Manifest