Games Board and Pieces
1650-1655 (made)
| Artist/Maker | |
| Place of origin |
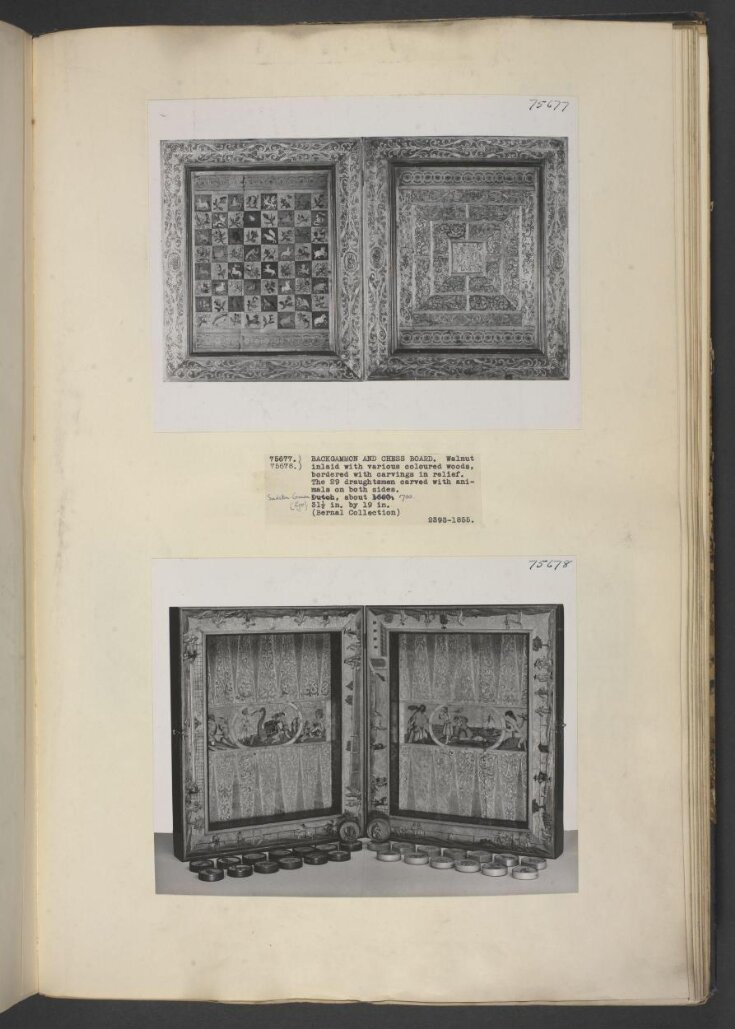
Backgammon and Chess Board. Of various coloured woods with burnt scrolls, the chequers of animals, birds, and flowers. The interior ornamented with groups of camels and figures, bordered with carvings in relief, coloured, of men playing at various games, containing 29 draughtmen, carved on both sides with animals
Object details
| Categories | |
| Object type | |
| Parts | This object consists of 29 parts.
|
| Materials and techniques | Painting, marquetry and carving. |
| Brief description | Backgammon and chessboard with gaming pieces, various coloured woods, English, Dutch or Hungarian, ca. 1660 |
| Physical description | Backgammon and Chess Board. Of various coloured woods with burnt scrolls, the chequers of animals, birds, and flowers. The interior ornamented with groups of camels and figures, bordered with carvings in relief, coloured, of men playing at various games, containing 29 draughtmen, carved on both sides with animals |
| Dimensions |
|
| Gallery label |
|
| Object history | Bought (Ralph Bernal Collection) £10 10s. 'English. About 1660' Provenance Ralph Bernal (1783-1854) was a renowned collector and objects from his collection are now in museums across the world, including the V&A. He was born into a Sephardic Jewish family of Spanish descent, but was baptised into the Christian religion at the age of 22. Bernal studied at Christ's College, Cambridge, and subsequently became a prominent Whig politician. He built a reputation for himself as a man of taste and culture through the collection he amassed and later in life he became the president of the British Archaeological Society. Yet the main source of income which enabled him to do this was the profits from enslaved labour. In 1811, Bernal inherited three sugar plantations in Jamaica, where over 500 people were eventually enslaved. Almost immediately, he began collecting works of art and antiquities. After the emancipation of those enslaved in the British Caribbean in the 1830s, made possible in part by acts of their own resistance, Bernal was awarded compensation of more than £11,450 (equivalent to over £1.5 million today). This was for the loss of 564 people enslaved on Bernal's estates who were classed by the British government as his 'property'. They included people like Antora, and her son Edward, who in August 1834 was around five years old (The National Archives, T 71/49). Receiving the money appears to have led to an escalation of Bernal's collecting. When Bernal died in 1855, he was celebrated for 'the perfection of his taste, as well as the extent of his knowledge' (Christie and Manson, 1855). His collection was dispersed in a major auction during which the Museum of Ornamental Art at Marlborough House, which later became the South Kensington Museum (now the V&A), was the biggest single buyer. |
| Subject depicted | |
| Association | |
| Bibliographic references |
|
| Collection | |
| Accession number | 2393:1 to 29-1855 |
About this object record
Explore the Collections contains over a million catalogue records, and over half a million images. It is a working database that includes information compiled over the life of the museum. Some of our records may contain offensive and discriminatory language, or reflect outdated ideas, practice and analysis. We are committed to addressing these issues, and to review and update our records accordingly.
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
| Record created | April 26, 2001 |
| Record URL |
Download as: JSONIIIF Manifest