Biblia pauperum
Print
ca. 1465 (printed), late 19th century - early 20th century? (bookbinding)
ca. 1465 (printed), late 19th century - early 20th century? (bookbinding)
| Artist/Maker | |
| Place of origin |
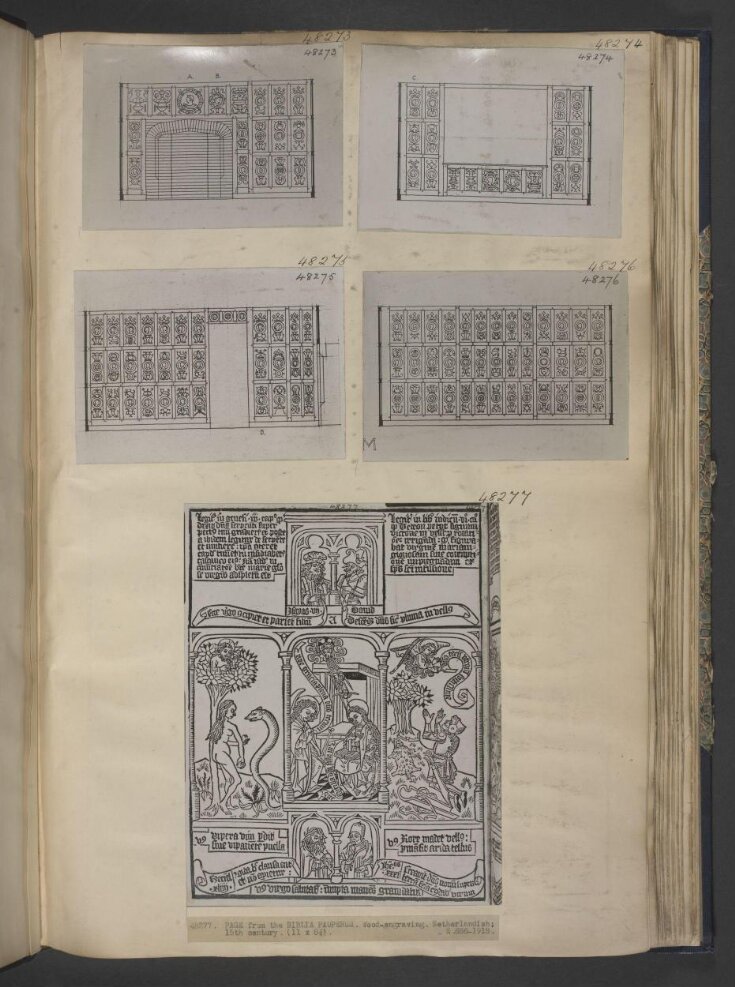
This page shows scenes from the New Testament flanked by parallel scenes from the Old Testament, with quotations at the top and bottom of the page from the Prophets. It comes from a block-book called the 'Biblia Pauperum' (Pauper's Bible). This name has been given to books which tell the story of the redemption of man by Christ, set against prophecies and prefigurations from the Old Testament.
Each page of a block-book, text and images, was carved from a single wood-block. The method was very laborious as the maker carved each line and letter out of the wood, cutting away the background. To make the print, paper was rubbed over the inked block from above.
Block-books were first made around 1430 and co-existed for decades with books printed with movable type (invented about 1450). This method was economical for very popular works because the block could print large numbers without expensive apparatus such as printing press or type.
Biblia Pauperum is a misleading name because the arrangement of texts explaining the images’ relationship to each other suggests an educated and pious readership. The book may have been intended for the poor clergy or as an aid for personal meditation.
Biblia Pauperum is thought to have been originally composed around the mid-13th century in the region that is now Austria and Southern Germany, evidence suggests, in monastic circles. More than 80 surviving manuscript versions have been identified (some in fragments), dating from around 1300 to the late 15th century.
Each page of a block-book, text and images, was carved from a single wood-block. The method was very laborious as the maker carved each line and letter out of the wood, cutting away the background. To make the print, paper was rubbed over the inked block from above.
Block-books were first made around 1430 and co-existed for decades with books printed with movable type (invented about 1450). This method was economical for very popular works because the block could print large numbers without expensive apparatus such as printing press or type.
Biblia Pauperum is a misleading name because the arrangement of texts explaining the images’ relationship to each other suggests an educated and pious readership. The book may have been intended for the poor clergy or as an aid for personal meditation.
Biblia Pauperum is thought to have been originally composed around the mid-13th century in the region that is now Austria and Southern Germany, evidence suggests, in monastic circles. More than 80 surviving manuscript versions have been identified (some in fragments), dating from around 1300 to the late 15th century.
Object details
| Categories | |
| Object type | |
| Title | Biblia pauperum (generic title) |
| Materials and techniques | Woodcut on paper in morocco leather binding, blind stamped |
| Brief description | Page from a bound block book called a Biblia Pauperum; Germany; ca. 1460; woodcut |
| Physical description | Page taken from a block book, inlaid and bound in a brown morocco leather binding, blind-tooled with all-over diamond pattern. In three horizontal compartments, the central compartment split into three vertically. In the central horizontal compartment a scene from the life of Christ, The Annunciation, is flanked on each side by a scene from the Old Testament: Eve and the Serpent to the left, and Gideon's Fleece to the right. In the centres of the top and bottom registers, four prophets wearing elaborate costumes and head-dresses sit beneath architectural archways (two above and two below). Speech scrolls contain quotations from the prophets. Clockwise from top left they are Isaias, David, Jeremias, Ezechiel. In the top horizontal compartment the two prophets are flanked either side by text explaining the connection between each of the two outer images and the central image. In the bottom horizontal compartment on either side of prophets are 'tituli', which serve as titles to the three main images. All text is in Latin. |
| Dimensions |
|
| Marks and inscriptions |
|
| Gallery label |
|
| Credit line | Bought under the terms of the Murray Bequest |
| Object history | Previous owner: Lieut. Lord Vernon, R.N., Sudbury Hall, Derbyshire. Historical significance: A block-book is a book where each page or double page spread, both text and images, is printed entirely from one wood block. The method of preparation of the block was very laborious. The maker had to cut each letter individually in the wood in reverse so only very popular works, such as summaries of the Bible, were printed in this way. The nature of blockbooks as printed from woodblocks enabled them to be printed in large numbers. Blockbooks were produced ca.1460 probably in Utrecht or Haarlem. Few were published after 1500. Biblia Pauperum is a name (in fact a misnomer accepted since Heinecken first used it in print in 1769) given to books which tell the story of the redemption of man by Christ, set against prophecies and prefigurations from the Old Testament. It is thought to have been originally composed around the mid-13th century in the region that is now Austria and Southern Germany, evidence suggests, in monastic circles. More than 80 surviving manuscript versions have been identified (some in fragments), dating from around 1300 to the late 15th century. Editions were also printed in blockbooks and moveable type. The blockbook consists of forty full-page illustrations united by an architectural frame. The pages are printed on one side only but these are paired so that they form double page openings. In illustrated versions of the Biblia Pauperum, scenes from important events in the New Testament (from the life of Christ or the Second Coming) are set together with four bust-length portraits of prophets and the texts of their prophecies that refer to the main event, as well as two narrative events from the Old Testament that prefigure the main event (except the last page which shows a scene from 'Revelations'). The text on each page consists of internally rhymed captions, called tituli, below the three pictures, the quotations from the four prophets appear as scrolls, and there are also exegeses of the two prefiguring scenes on either side of the central image. "Typology is rooted in textuality and the literal meaning of Scripture" and thus "cannot have been intended (as some have claimed) for an unlettered audience". Sometimes the reader is required to remember or make reference to the scriptures. Allegory is included in the imagery and even parallel arrangement of people and objects in the images or is spelled out in the exegeses. Most of the tituli tell the story of the types. The exegeses do too, but also tell how the types relate to the antitype. (quotes from Nellhaus, Tobin, pp. 296-297.) "It is probably not coincidental that the blockbook versions of the Biblia Pauperum appeared around the same time that numerous treatises on the Art of Memory were also published, whether with woodcuts or movable type. New technologies of communication are often used at first to amplify old patterns of thought. Understood in this way, early print culture and especially blockbook culture initially reinforced the interaction of oral and literate strategies that characterised the later Middle Ages. Thus the blockbook, which, like the printing press, was an innovation in the production of writing, was also a final, complex elaboration of medieval conceptual strategies." (Nellhaus, Tobin, p. 321.) "The manuscript version of the Biblia Pauperum is the earliest illustrated book of typology and in both its manuscript and blockbook forms the book had a profound and enduring effect on the typological tradition. Typology is in fact absolutely fundamental to the Biblia Pauperum: it is virtually the book's sole principle of composition." (Nellhaus, Tobin, p. 294) Typology in this context (it is sometimes used more broadly) is "a habitual strategy of thought or conceptual composition, which shows how people or events in the Old Testament (the types) prefigure and are fulfilled by people or events in the Gospels (the antitypes). Historically, typological prefiguration was closely associated with Christianity from its beginnings, and it greatly proliferated in the twelfth century. ... Along with typology, the types and antitypes are frequently portrayed with visual analogues; some individual images have allegorical content and the power of symbolic objects appear in several scenes". (Nellhaus, Tobin, p. 296) Thus, allegory and symbolism interconnect in this work. quotations from Nellhaus, Tobin. 'Mementos of Things to Come: Orality, Literacy, and Typology in the Biblia Pauperum' in Hindman, Sandra. Printing the Written Word: The Social History of Books, circa 1450-1520. London, 1991, pp. 292-321. |
| Historical context | see Henry, Avril. Biblia Pauperum. Scolar, 1987, p. 50 for more in-depth analysis. Nellhaus, Tobin. 'Mementos of Things to Come: Orality, Literacy, and Typology in the Biblia Pauperum' in Hindman, Sandra. Printing the Written Word: The Social History of Books, circa 1450-1520. London, 1991. |
| Production | Edition belongs to Groupe IV, No. 10 in Schreiber (see references). Weimar Group (i.e. edition XI)- see Renate Kroll's essay p289-310 in Blockbücher des Mittlealters (see references) discussing reengraving of plates 29 and 30. |
| Subjects depicted | |
| Place depicted | |
| Literary references |
|
| Summary | This page shows scenes from the New Testament flanked by parallel scenes from the Old Testament, with quotations at the top and bottom of the page from the Prophets. It comes from a block-book called the 'Biblia Pauperum' (Pauper's Bible). This name has been given to books which tell the story of the redemption of man by Christ, set against prophecies and prefigurations from the Old Testament. Each page of a block-book, text and images, was carved from a single wood-block. The method was very laborious as the maker carved each line and letter out of the wood, cutting away the background. To make the print, paper was rubbed over the inked block from above. Block-books were first made around 1430 and co-existed for decades with books printed with movable type (invented about 1450). This method was economical for very popular works because the block could print large numbers without expensive apparatus such as printing press or type. Biblia Pauperum is a misleading name because the arrangement of texts explaining the images’ relationship to each other suggests an educated and pious readership. The book may have been intended for the poor clergy or as an aid for personal meditation. Biblia Pauperum is thought to have been originally composed around the mid-13th century in the region that is now Austria and Southern Germany, evidence suggests, in monastic circles. More than 80 surviving manuscript versions have been identified (some in fragments), dating from around 1300 to the late 15th century. |
| Bibliographic references |
|
| Collection | |
| Accession number | E.686-1918 |
About this object record
Explore the Collections contains over a million catalogue records, and over half a million images. It is a working database that includes information compiled over the life of the museum. Some of our records may contain offensive and discriminatory language, or reflect outdated ideas, practice and analysis. We are committed to addressing these issues, and to review and update our records accordingly.
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
You can write to us to suggest improvements to the record.
Suggest feedback
| Record created | December 19, 2006 |
| Record URL |
Download as: JSONIIIF Manifest